Next week–January 21st–we’ll be looking at the debate between cultural and rationalist approaches to the analysis of political phenomena. As Whitefield and Evans note in the abstract of their 1999 article in the British Journal of Political Science:
There has been considerable disagreement among political scientists over the relative merits of political culture versus rational choice explanations of democratic and liberal norms and commitments. However, empirical tests of their relative explanatory power using quantitative evidence have been in short supply.
Their analysis of the political attitudes of Czech and Slovak residents is relatively rare in that the research is explicitly designed to assess the relative explanatory purchase of cultural and rationalist approaches to the study of political phenomena. Whitefield and Evans compile evidence (observational data) by means of a survey questionnaire given to random samples of Czech and Slovak residents. In order to assess the strengths of rationalist versus cultural accounts, Whitefield and Evans use statistical regression analysis. Some of you may be unfamiliar with statistical regression analysis, This blog post will explain what you need to know to understand the regression analysis results summarised in Tables 7 through 9 in the text.
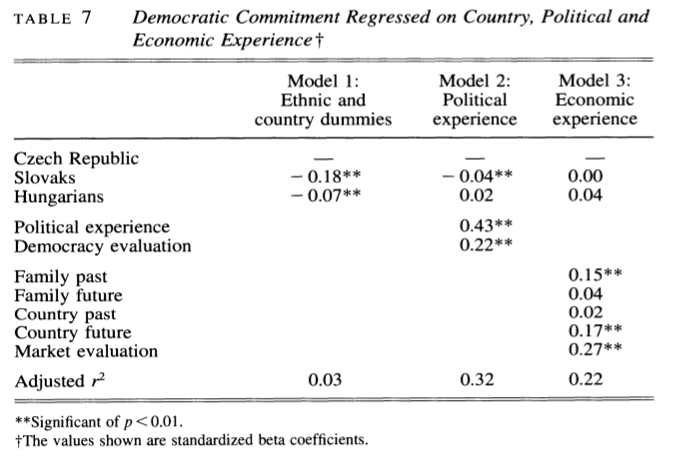
Let’s take a look at Table 7. Here the authors are trying to “explain” the level of “democratic commitment”–that is, the level of commitment to democratic principles–of Czech and Slovak residents. Thus, democratic commitment is the dependent variable. The independent, or explanatory, variables can be found in the left-most column. These are factors that the authors hypothesize to have causal influence on the level of democratic commitment of the survey respondents. Some of these are nationality–Slovaks, Hungarians, political experience and evaluations–past and future–of the country’s and family’s well-being.
Each of the three remaining columns–Models 1 through 3–represents the results of a single statistical regression analysis (or model). Let’s take a closer look at the first model–ethnic and country dummy variables. In this model, the only independent variables analysed are one’s country and/or ethnic origin. The contrast category is Czechs, which means that the results are interpreted relative to how those of Czech residence/ethnicity answered. We see that the sign for the result of each of the two explanatory variables–Slovaks and Hungarians–is negative. What this means is that relative to Czechs, Slovaks and Hungarians demonstrated less democratic commitment. The two ** to the right of the numerical results (-0.18 and -0.07, respectively) indicate that this result is unlikely to be due to chance and is considered to be statistically significant. This would suggest that deep-seated cultural traditions–ethnicity/country or residence–have a strong causal (or correlational, at least) effect on the commitment of newly democratic citizens to democracy. Does this interpretation of the data still stand when we add other potential causal variables, as in Models 2 and 3? What do you think?







You must be logged in to post a comment.