[UPDATE: I made a mistake when I was initially tabulating results, necessitating a slight change in the composition of the Bundestag. As it now stands, the problem occurred in West Land, where is seems some poll workers had imbibed a little bit too much of that noted Bavarian beverage, bier. A recount (which is easy given that paper ballots were used) results in the following change: one more mandate for the FDP in West Land–I’ve slotted in the 4th candidate from the FDP party list from that Land–and one fewer mandate for the SPD in the same Land. Therefore, the final results are FDP-6; CDU-4; Greens-3; SPD-3. The party leader of FDP will still be given the role of party formateur.]
[UPDATE 2: The aforementioned poll workers have been fired and are now in AA.]
[UPDATE 3: Please see below how the adviser roles have been distributed.]
Here are the results from the mock election to the lower house of the German Reichstag held this afternoon. Those of you who were not elected to represent your district or Land in the Bundestag will nonetheless also be actively involved (as advisers to your fellow party members) in the second part of the simulation–negotiations to form a government. I will send more instructions regarding that portion of the simulation later this weekend. As you can see below, the FDP has won a plurality in the Bundestag and will be given first crack at putting together a workable coalition, trying to reach a formal agreement with one of the other parties. Signing coalition agreements with either the CDU/CSU or the SPD are most likely (given that there is a total of 16 seats in our parliament) but don’t count out a coalition with the Greens either.
As I mentioned earlier, I’ll have more information regarding the specifics of the coalition negotiations and also post a sample coalition agreement form on Blackboard later, but in the meantime think about the most important elements of the negotiation process:
- Which party/parties will form the government? Remember you need a majority in parliament to vote the new government into power.
- Who will become the Chancellor (i.e., the Prime Minister)?
- What will be the general orientation of the government’s policy-making agenda? Given the campaign pledges you made (either to your district and/or your Land) can you plausibly vote for a government that is dedicated to carrying out this policy agenda?
- What about some of the policy specifics? Changes to the citizenship law? Higher taxes on carbon emitting industries? Higher (lower) income/consumption taxes? Anything else of importance to you or your district/Land?
- Who will get which Ministerial Portfolios? Who will become Foreign Minister? Minister of the Environment? Minister of Health? Minister of Finance? Minister of Justice? Minister of Labor?
- Which individuals will be given these portfolios?
I will set up a new folder in the Discussion Board section of Blackboard so that you can all begin the “feeling out” process prior to the official negotiations on Tuesday afternoon.
Click here to see the current members of the German Federal Cabinet (which is the Chief Executive), which is made up of the Chancellor (currently Angela Merkel) and 15 Cabinet ministers.
NOTE: You will notice that some of you who ran for election in districts have nonetheless been elected to parliament on the basis of party lists. I had to do this, given the relatively small number of students in the class. In general, the party lists are much larger than the ones you saw on your ballots as there were simply not enough students and I wanted to have four SMDs. Therefore, where it was warranted, I moved non-SMD-winners over to party lists (i.e., when the proportion of votes generated a number of seats for that party in excess of the number of individuals on the party list. Of course, this would never happen in a real German election as the party lists always have many more candidates than the party will end up earning on the basis of PR. I’ll go over this on Tuesday.
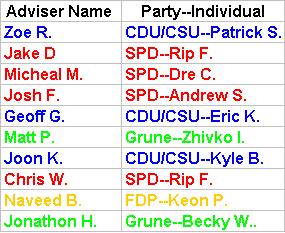
Here are the advisers and the party member whom you will be advising over the course of the government formation negotiations on Tuesday.









You must be logged in to post a comment.