Charlie Rose interviews Huntington on the ideas in his oft-cited and even more criticized “Clash of Civilizations” thesis. Rose calls the clash thesis “provocative.” What do you think about the logic of the clash thesis. Given that you’ve read Amartya Sen’s response to Huntington, what kinds of questions would you have asked Huntington that Rose failed to? (The Huntington interview runs from 1:55 until about 21:00. No, Professor Huntington is not a dead-ringer for John Cleese. That is, in fact, John Cleese, who is interviewed in the middle segment; hence, the screen shot of Cleese.)
Category: IR Theory
Results from a Prisoner’s Dilemma Simulation–The Oil Game
Today in class, you competed in groups to maximize total profits in a simulation called “the Oil Game.” You represented one of two competing oil producers–Iraz and Sabia–trying to maximize profits selling oil to a net importer of oil–ESYUVI (the names were created using a random letter-generator–I swear!). Most of you recognized very quickly, if not immediately, that the simulation was a modified Prisoner’s Dilemma situation. As I’ll discuss on Friday, in a Prisoner’s Dilemma situation, players acting in an instrumentally rational manner will always choose not to cooperate (i.e., “defect”), because it is a dominant strategy. What makes the situation a dilemma is that the players could do much better were they able to cooperate and trust one another.
The compelling logic of the prisoner’s dilemma, along with some strong empirical evidence, is used by realists to support their arguments regarding the nature of interaction in the international world. Liberals, on the other hand, argue that there is much more cooperation in the world than realists would predict. Thus, despite the structure of the prisoner’s dilemma, players are able to cooperate in international politics. What factors do you think make cooperation more likely? Less likely? Why?
The results from our simulation today are in graphical form above. You’ll note that communication was not allowed for Years 1, 2, and 4; communication was allowed for Year 3, and communication (to decide what to do for Years 5 and 6) was allowed prior to Year 5. The results from this class are consistent with the expectations. I would note the relatively low level of cooperation throughout, rising only initially after the first episode of communication.
Pearl Jam and R.E.M
If I had to guess as to which theory of international relations the lead singers of two of my favorite bands, Eddie Vedder (Pearl Jam) and Michael Stipe (R.E.M.) would subscribe, I’d say radicalism, and radicalism, respectively. Here’s a version of what can only be characterized correctly as a protest song, Begin the Begin, from one of R.E.M.’s earliest albums. The lyrics are below. There’s certainly no compromise in this song; they argue, like all radicals, for radical systemic change; if you don’t like the system, “begin the begin.”
(chorus)
Birdie in the hand for life’s rich demand
The insurgency began and you missed it
I looked for it and I found it
Myles Standish proud, congratulate meA philanderer’s tie, a murderer’s shoe
Life’s rich demand creates supply in the hand
Of the powers, the only vote that matters
Silence means security silence means approval
On Zenith, on the TV, tiger run around the tree
Follow the leader, run and turn into butterLet’s begin again, begin the begin
Let’s begin again like Martin Luther zen
The mythology begins the begin
Answer me a question I can’t itemize
I can’t think clear, you look to me for reason
It’s not there, I can’t even rhyme here in the beginA philanderer’s tie, a murderer’s shoe
Example: the finest example is you(repeat chorus)
A philanderer’s tie, a murderer’s shoe
Let’s begin again, begin the begin
Let’s begin again
Individuals Having an Impact on IR
In a previous post, I asked you to consider not how international relations affects you, but how the way in which you behave, and the actions that you take have an effect on IR. Here’s a story about how changing individual attitudes in Japan may be having a greater impact on the whaling industry than the combined efforts of states and NGOs over the last couple of decades. You can see a graphically disturbing video of whales being killed at the link above.
JAPAN’s whalers are going broke and have been forced to slash prices because no one wants to eat their growing mountain of whale meat.
The farcical truth of Japan’s whaling industry was exposed yesterday by Japanese media reports that the Institute for Cetacean Research is struggling to repay $37 million in government subsidies.
The report came as Japanese embassy officials made a stern protest in Canberra over the Federal Government’s release of shocking whaling photographs.
The ICR, responsible for Japan’s lethal “research operation”, is flooding Japan with cheap whale meat that it cannot sell, according to the reports in respected newspaper Asahi Shimbun.
Meat and other parts of whales killed during ICR “scientific research” in the Southern Ocean is sold to a private fisheries company Kyodo Senpaku, which manages the sale of whale meat in the Japanese market. But while ICR has consistently increased the number of whales it kills – by 30 per cent between 2005 and 2006 – there has been no rise in domestic demand for whale meat or products.
Greenpeace Australia Pacific whales campaign director Rob Nicholl said the losses were further proof that there was no market for whale meat in Japan.
“It’s standard economics. There is an oversupply. They’ve had to reduce the price but they still can’t get rid of the stuff,” he said.
Do you think that this story can shed any light on a potential solution to the drug and human trafficking industries? How specifically?
Condoleeza Rice, International Relations Theory and the Bush Administration
In class today, I tried to convince you that understanding IR from a theoretical perspective was not simply some abstract, pedantic pursuit, but that the theoretical lens through which we view international relations does have real-world implications, many of which are dramatic.
I noted the role of Condoleeza Rice as the chief National Security Advisor to President Bush during his first term and also noted that Rice has long held a realist view of international relations. As you must know by now (I think I’ve mentioned it about 503 times since the beginning of the semester), realists view the state as the only prominent actor in international affairs. This was Rice’s view upon assuming her new position and this was manifested in the security objectives of the incoming administration, which did not believe, initially, that a non-state actor like Al Qaeda was a grave threat to the security of the United States.
Here are excerpts from Rice’s article in Foreign Affairs magazine in the midst of the 2000 presidential election campaign:
Summary: With no Soviet threat, America has found it exceedingly difficult to define its “national interest.” Foreign policy in a Republican administration should refocus the country on key priorities: building a military ready to ensure American power, coping with rogue regimes, and managing Beijing and Moscow. Above all, the next president must be comfortable with America’s special role as the world’s leader…
Continue reading “Condoleeza Rice, International Relations Theory and the Bush Administration”
“Who” is China? A Constructivist Approach to Security
William A. Callahan is a fellow at the Woodrow Wilson Center for International Scholars who is currently working on a project that links Chinese notions of self-identity and that country’s broader security environment. As you may have guessed, Callahan approaches the topic from a constructivist perspective, in which issues of culture and identity are paramount. A realist would never ask “who” is China, but “what” is China. Here’s a snippet:
Who is China? This question is fundamental to the internal debate among Chinese elites as they grapple with national identity which, in turn, affects policy decisions…culture and history are intimately linked to China’s current foreign policy outlook.
Callahan’s book project analyzes how history, geography, and ethnicity shape China’s relations with the world. “To understand this, we must look at how China relates to itself,” he said. “China’s national security is closely tied to its national insecurities.”
One such insecurity is its shame over lost territory. Callahan cited “national humiliation maps” that outline historical China’s imperial boundaries juxtaposed with present-day borders. “These maps, which are produced for public consumption, narrate how China lost territory to imperialist invaders in the 19th century—especially Taiwan to Japan and the North and West to Russia,” said Callahan. “China lost a large chunk of territory. The humiliation—and how to cleanse it—is an important point that shapes China’s nationalism and pride.”
In fact, most demonstrations in China about any given problem usually have a historical aspect, he said, such as in 1999, when the United States bombed the Chinese Embassy in Belgrade, which was viewed in China as a humiliation similar to those of a century ago at the hands of the West.
“Idealized versions of China’s imperial past are now inspiring Chinese scholars’ and policymakers’ plans for China’s future—and the world’s future—in ways that challenge the international system,” said Callahan. This makes the study of identity politics all the more critical.
China and Japan, for example, have close economic relations but cool social and political ties. Callahan said, “China relates to Japan as an evil state, recalling World War II atrocities, such as the Nanjing massacre, and this memory has taken over the relationship.”
Notice the importance of the premise in the penultimate paragraph: that “idealized versions of China’s past” (i.e., culture and identity) are having a causal impact on China’s foreign policy. This contrasts starkly with realist conceptions of the nature of international relations. Below are two diagrams from Shih demonstrating the difference between realist and constructivist conceptions of security.
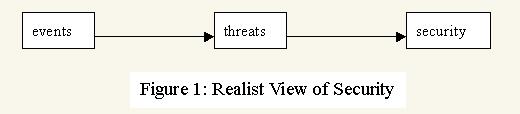
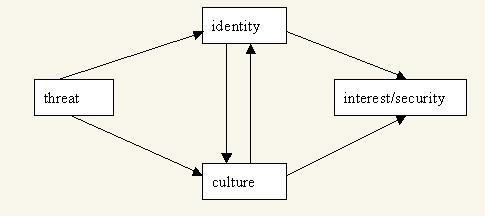
Notice that the impact of threats on security is not direct in the constructivist view; rather, it is mediated by culture and identity, both of which also affect each other.
American Conservatives Against John McCain’s Foreign Policy
A few sessions from now we’ll analyze international relations from a state-level perspective. The great debate in IR, with respect to the state level, is whether state level characteristics such as economic system, political regime, etc., are determinative in explaining and predicting state behavior at the international level. As we have already discussed, the neorealists have a ready answer: the only state-level characteristic that matters in foreign affairs is power. The liberals, of course, have a different viewpoint, as do radicals and constructivists. Notice one word that was absent from the preceding two sentences–conservative. What are the elements of a conservative foreign policy? [There is, of course, a neoconservative approach (or theory) in IR, but what about conservative, with the neo prefix? Moreover, does the ideological viewpoint of the U.S. President matter in the way that foreign policy decisions in the White House are made?
To help answer the second question, I would like to introduce you to a group of self-professed American conservatives, who banded together in 2002 and created The American Conservative magazine. How do those in charge of the magazine define conservatism and what are their views of the upcoming presidential election?
We believe conservatism to be the most natural political tendency, rooted in man’s taste for the familiar, for family, for faith in God. We believe that true conservatism has a predisposition for the institutions and mores that exist. So much of what passes for contemporary conservatism is wedded to a kind of radicalism—fantasies of global hegemony, the hubristic notion of America as a universal nation for all the world’s peoples, a hyperglobal economy. In combination with an increasingly unveiled contempt for America’s long-standing allies, this is more a recipe for disaster.
Against it, we take our stand.
Consistent with their view of conservatism, they are worried (terrified?) with the prospect of a McCain presidency. Rather than excerpt from a recent article in the magazine that assesses what a President McCain means for the future of American foreign policy, I’ll provide a link to the article and give you the title and a shot of the cover:
“The Madness of John McCain–A militarist suffering from acute narcissism and armed with the Bush Doctrine is not fit to be commander in chief.”

Drezner explains Neo-conservatism
Here‘s a nice, and concise, description from Dan Drezner* of neo-conservatism, the theoretical underpinning of the Bush administration’s foreign policy.
Neo-conservatism borrows many ideas from liberal internationalism, though it promotes those ideas in terms of more expansive aims and aggressive methods. The first sentence of the March 2006 National Security strategy reads, “It is the policy of the United States to seek and support democratic movements and institutions in every nation and culture, with the ultimate goal of ending tyranny in our world.” Like liberal internationalists, neo-conservatives believe that the spread of free markets, democratic values, and human rights leads to a more prosperous and pacific world. But neo-conservatives reject the “third leg” of the Kantian triad: multilateralism. Whereas liberals put greater faith in international institutions as a means of promoting American interests, neo-conservatives view them as constraints on US action: in place of multilateral agreements, neo-consevatives prefer more unilateral and more forceful means of promoting regime change.
*If you are interested in international political economy, you should take a look at Drezner‘s blog. You also may be interested in his new book–Daniel W. Drezner, All Politics Is Global Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2007).
The Future of US Foreign Policy post-Bush?
Daniel Drezner, an associate professor of international politics at the Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy at Tufts University, has published an article in the latest issue of Internationale Politik und Gesellschaft (“International Politics and Society”) entitled “The Future of U.S. Foreign Policy.” In it he envisions what a post-Bush US foreign policy (regardless of which party wins the White House) should look like.
As we have already discussed, and will discuss further throughout the course, a fundamental tenet of the realist theory of international relations is that the nature of the domestic regime does not matter as it pertains to the manner in which a state acts in the world. Thus, whether a regime is democratic, authoritarian, or even a theocracy, the compelling logic of trying to ensure security in an anarchic world means that all states will act the same way. A corollary of that is that it does not matter, say the realists, whether the leadership of a state is more left-wing or more right-wing, the fundamental character of foreign policy will be the same. Does Drezner agree with the realists?
For Europe, American foreign policy in 2009 will clearly be an improvement on its current incarnation. Regardless of who wins the presidential election, there will likely be a reaching out to Europe as a means of demonstrating a decisive shift from the Bush administration’s diplomatic style. This does not mean, however, that the major irritants to the transatlantic relationship will disappear. On several issues, such as GMOs or the Boeing–Airbus dispute, the status quo will persist. On deeper questions, such as the use of force and the use of multilateralism, American foreign policy will shift, but not as far as Europeans would like. When George W. Bush leaves office, neo-conservatism will go with him. This does not mean, however, that Europeans will altogether agree with the foreign policy that replaces it.
Drezner also has some interesting things to say about neoconservatism, the theory underpinning the Bush administration’s view of international relations:
It would appear that Americans are now disenchanted with neo-conservatism
as a foreign-policy doctrine. Five years ago, the idea of muscular,
unilaterally-imposed democratization was believed to resonate with
American values in a post-9/11 world. This is no longer the case. In October
2006, a Public Agenda poll found that 83 % of Americans are worried
about the way things are going for the United States in world affairs.
Their new »Anxiety Indicator« found that »a significant majority of the
public is feeling anxious and insecure about the country’s place in the
world.« Iraq – an obsession of neo-conservatives for over a decade now –
is obviously a major cause of this discontent……Neo-conservatism will formally expire as the grand strategy of the
United States on January 20, 2009: the date George W. Bush leaves office.
What will take its place? There are myriad ways in which us foreign
policy could diverge from the neo-conservative approach.

